Did you know that achieving healthy lawn growth depends on how well you infuse nutrients into the soil? That’s right, a basic understanding of lawn nutrient importance directs you to the proper quality that supports growth, color, strength, and disease resistance in grass. Learning these lawn vitality basics is necessary for balance because each nutrient has a unique purpose. Balanced nutrition is key to maintaining rich lawn density and overall health.
So, whether it’s for overall growth or specific needs like stronger root systems, richer greenness, or disease resistance, this grass nutrition guide has all the answers you seek.
Key Nutrients Every Lawn Needs
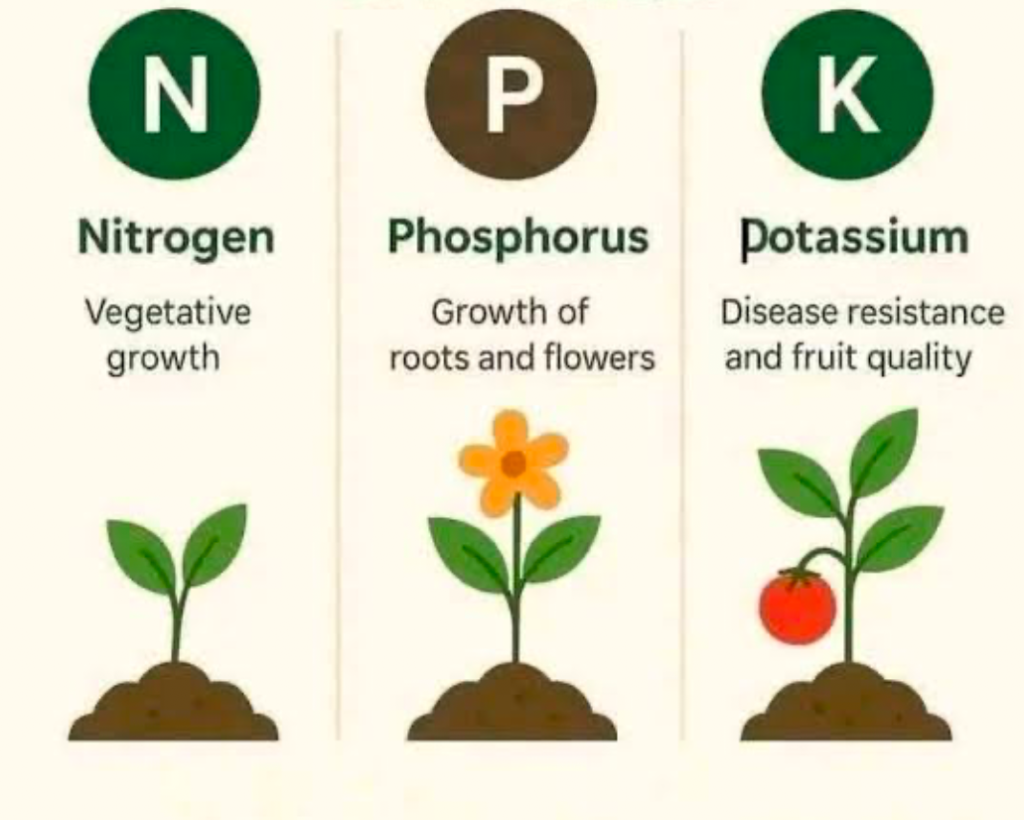
We’ll start with the three essential lawn nutrients, namely nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are responsible for greenness, root growth, and density.
When you see “NPK nutrients” listed on fertilizer packages, it’s referencing these three macronutrients that contribute to a lawn’s healthy growth. Here’s a summary of the grass nutrient needs each one covers:
- nitrogen(N): Leaf growth
- Phosphorus (P): Root development and plant energy transfer
- Potassium (K): Disease resistance
Understanding lawn fertilizer basics ensures a balance and proper application of the nutrients your lawn needs. So here’s a detailed breakdown.
Nitrogen: The Growth Booster

Nitrogen is a lawn greening nutrient because it helps form chlorophyll, which is used for photosynthesis and energy production in your grass.
Use fertilizer with high nitrogen for lawns when you need to boost growth, improve leaf structure, and ensure a rich green appearance. Be careful, though, because these nitrogen benefits can become harmful when there is excess.
Excess nitrogen burns the roots by increasing soil acidity and encouraging pest activity. When this leaf growth booster leaks into the surrounding water, it pollutes the environment and creates dead zones. So, stick to regulated application rates.
Phosphorus: Root Development Champion

Use phosphorus for grass, flower,and root strength development, seedling establishment, and nutrient absorption. If you notice purpling leaves, slow flowering, and patched spots from light foot traffic, then it’s time to add this root development nutrient into your soil.
It’s a great nutrient forlawn seeding support because it increases root hairs, anchors seedlings in the soil, and promotes dense sprouts.
Despite these phosphorus benefits, excessive use causes nutrient imbalance, run-offs, and stunted growth.
Potassium: The Resilience Builder

If you need a drought-tolerance nutrient, then potassium is the answer.It works for disease resistance, lawn stress resistance, and recovery by strengthening cell walls and encouraging better nutrient uptake.
Using potassium for lawns helps protect your grass from harsh weather, including heat and winter. With stronger cell walls in the soil, there’s less risk of diseases like snow mold and burning roots.
So, infuse potassium into your soil as an overall grass health support nutrient, but ensure balanced levels by following the instructions on the package.
Micronutrients: The Unsung Heroes

NPK macronutrients are popular, but people often forget lawn micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese, which also affect grass color, growth, and enzyme activity.
Here are some micronutrient benefits for your lawn:
Iron (Fe)
Use iron for green grass, just like you do with nitrogen, since it also helps make chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Zinc (Zn)
Zinc regulates leaf growth and, together with phosphorus, promotes stronger root development.
Manganese (Mn)
Manganese stimulates enzyme activity, boosting nitrogen and iron levels and promoting more chlorophyll production.
So you see that even the slightest deficiency of a minor nutrient need can impact grass color, growth, and enzyme function.
Signs Your Lawn Is Nutrient Deficient
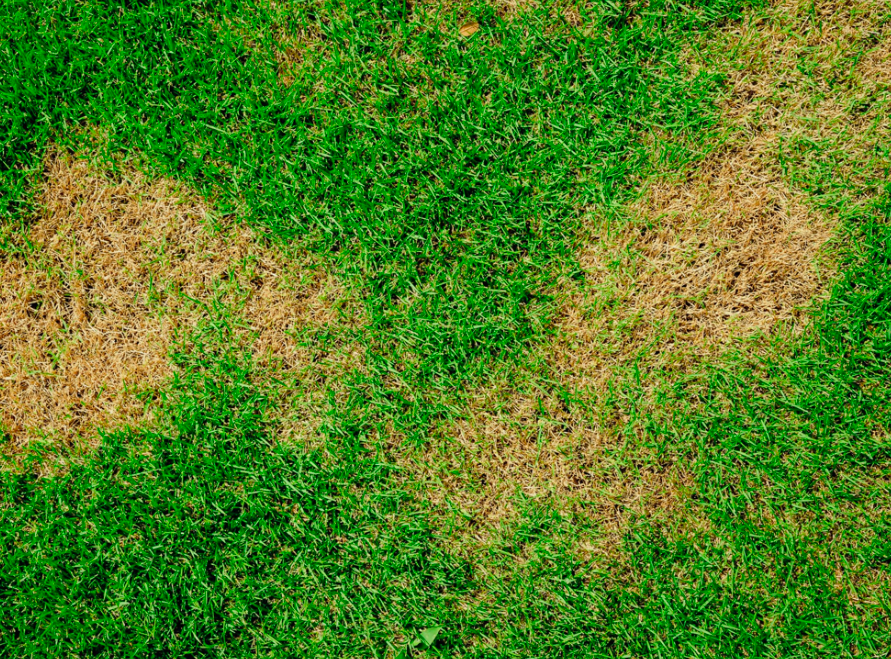

Look out for nutrient deficiency signs such as yellowing, patchy growth, discoloration, slow growth, or increased weeds, and immediately repair your lawn.
Discoloration (Yellow Grass)
Discoloration in grass is called chlorosis, and it often appears as yellowing leaves, but sometimes it’s also brown or purple. It’s one of the most obvious signs if nutrient deficiency because it affects the lawn’s appearance.
Identify yellow-grass causes and triggers to ensure corrective and preventive actions. Nitrogen and iron deficiency are the leading causes of yellow chlorosis, while a lack of phosphorus causes purple or red blades.
Patchy Growth
With poor root systems and heavy foot traffic, you’ll face patchy lawn issues. When your soil lacks phosphorus and zinc, grasses can uproot easily, leaving the soil bare.
Slow Growth
Slow growth, unlike patchy growth, is caused by potassium deficiency. It also causes poor stress recovery from uprooted blades.
Increased Weeds
Ignoring these poor lawn health symptoms leads to bigger problems, like increased weeds and pests growing in sparse areas without the strong nutrients to battle them.
Different Types of Fertilizers and When to Use Them

Explore different lawn feeding options to correct nutrient deficiency in your soil. But first, test the soil to identify the nutrient needs, then choose an appropriate fertilizer.
There are many lawn fertilizer types, but they all fit into two broad groups depending on their composition. You can use organic or synthetic fertilizer, depending on your preference, as both have benefits and drawbacks that affect their use.
Here’s a comparison to help you choose.
Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizer
Organic fertilisers are made from natural materials such as animal and plant matter, while synthetic fertilisers are chemical-based. Both can be in liquid or dry form and have specific nutrient properties that support targeted repairs.
With organic fertilisers, the results are slow but lasting, while synthetic fertilisers work faster but only have short-term effects.
Choose organic fertilizers for longer-lasting results, while synthetic fertilizers work for quick aesthetic boosts.
Keep reading for another fertilizer comparison to guide your choice.
Slow-Release vs. Fast-Release Options
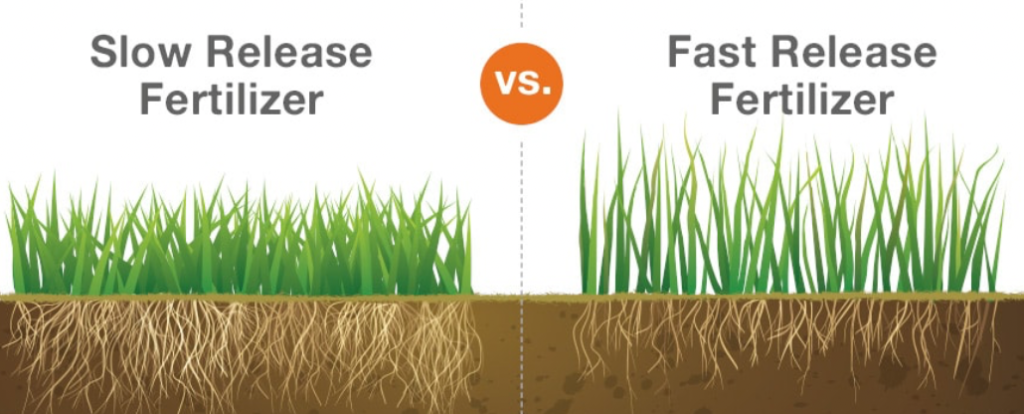
With a slow-release fertilizer, nutrients break down in the soil over a long period, which supports slow but steady growth. Meanwhile, a fast-release fertilizer provides a quick boost to your soil.
Understanding the differences between these nutrient delivery methods is important for repairing damaged lawns, as you need to choose a method based on what your grass needs.
Here’s a fertilizer timing guide to help you:
For new seedlings and plants, slow-release fertilizers are the best. They give your soil time to absorb the macro- and micro-nutrients necessary for steady, healthy growth.
But if you want a quick boost for a patchy lawn that’s not damaged to the roots, then a fast-release fertilizer works better.
Creating a Fertilization Schedule for Optimal Health

Follow a seasonal lawn fertilisation schedule to restore nutrient-deficient soil and achieve optimal results. If you don’t have any seasonal fertilizing timing tips, don’t worry. Here are some practical tips to guide you through the process.
As a general rule, feed your lawn with a nitrogen-rich fertilizer mix in early spring to support the natural growing season. Phosphorus-rich fertilizers are better in the summer to discourage weed growth, while potassium-rich mixes are best for fall and winter to winterize the lawn ahead of frosty weather.
Another underrated part of the generallawn feeding guide is the grass type identification. Note your grass species, whether it’s a warm-season or cold-season strain, and choose the right time for feeding.
Seasonal lawn care is important since weather and climate conditions affect grass growth and development.
Incorporating Soil Testing into Your Lawn Care Routine
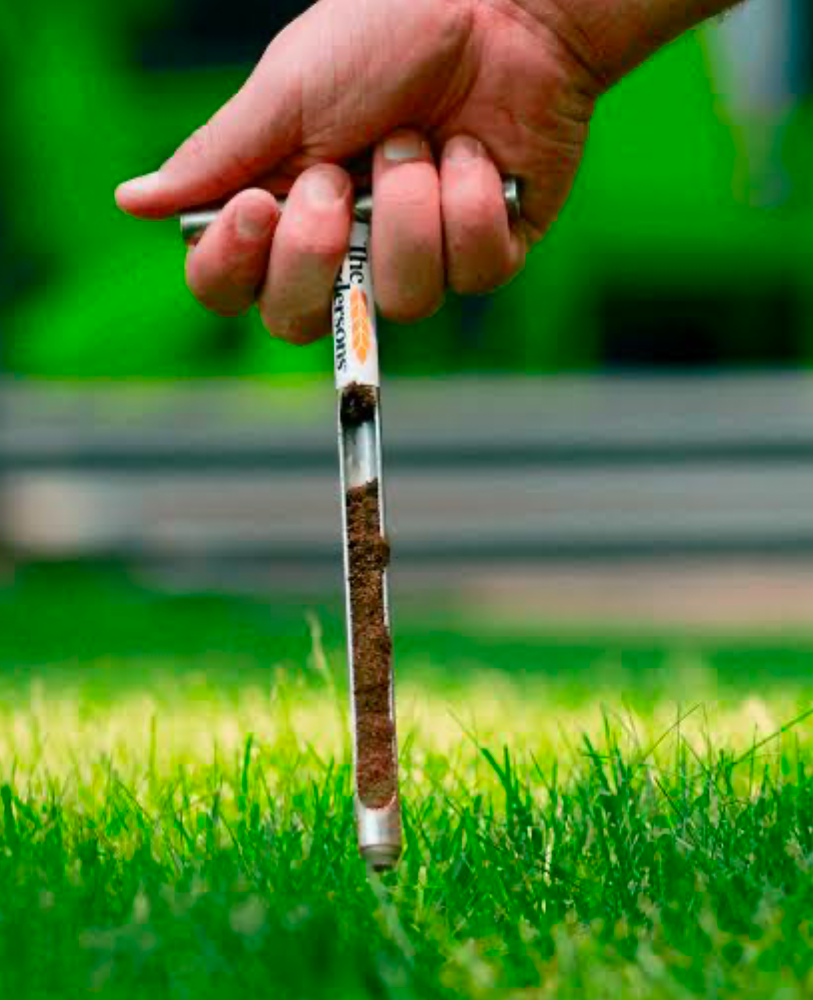

Periodic soil testing for lawns is a more accurate way to determine nutrient levels, pH, and deficiencies.
Your lawn’s pH levels show how much acidity or alkalinity is in the soil. Use a simple test kit for compact lawns, but send samples to professional labs for advanced soil nutrient analysis on larger lawns.
Make a yearly habit of testing lawn soil samples for nutrient levels, pH, and deficiencies for accurate results without overstretching your account.
Balancing Your Lawn’s Nutrient Needs with Natural Practices

Practicing natural lawn care with traditional methods like mulching, composting, and overseeding supports soil health by producing micro and macronutrients.
Composting
Prepare organic compost for grass lawns by combining browns, greens, and a diverse mix of natural animal- or plant-based matter to replenish lost soil nutrients. Apply a top dressing of compost at the base of the grass to improve soil structure and encourage microbial activity.
Mulching
Mulching benefits your lawn year-round by protecting the soil from harsh heat and frost. Cover your grass with grass clippings to prevent weeds.
Overseeding
Discourage weeds with overseeding to cover patches and areas of stunted growth.
When you combine these organic lawn practices with proper fertilization, you’ll have fewer problems with nutrient deficiency or excessiveness.
Conclusion: Cultivating a Thriving Lawn with Essential Nutrients
After reading this lawn care summary on nutrients necessary for healthy growth and appearance, you should be able to manage your lawn successfully. Remember that the key to this healthy grass guide is to create a proper nutrient balance so that you can meet every part of your lawn’s needs.
Follow the nutrient care tips in this guide from testing your soil to observing your grass to determine the deficiency it’s suffering and correct it immediately. Check the NPK and micronutrient ratio before feeding your lawn. Use a seasonal feeding schedule and seal the results with aftercare. If you take this thriving lawn advice, you’ll have an improved, healthier, and nutrient-rich lawn in at least three months.


